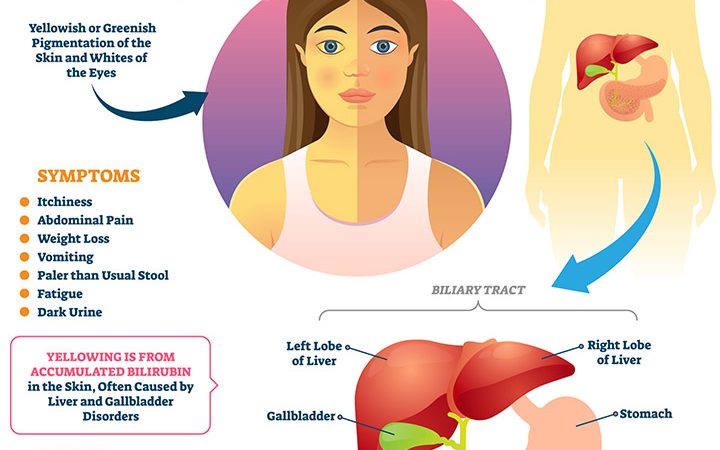
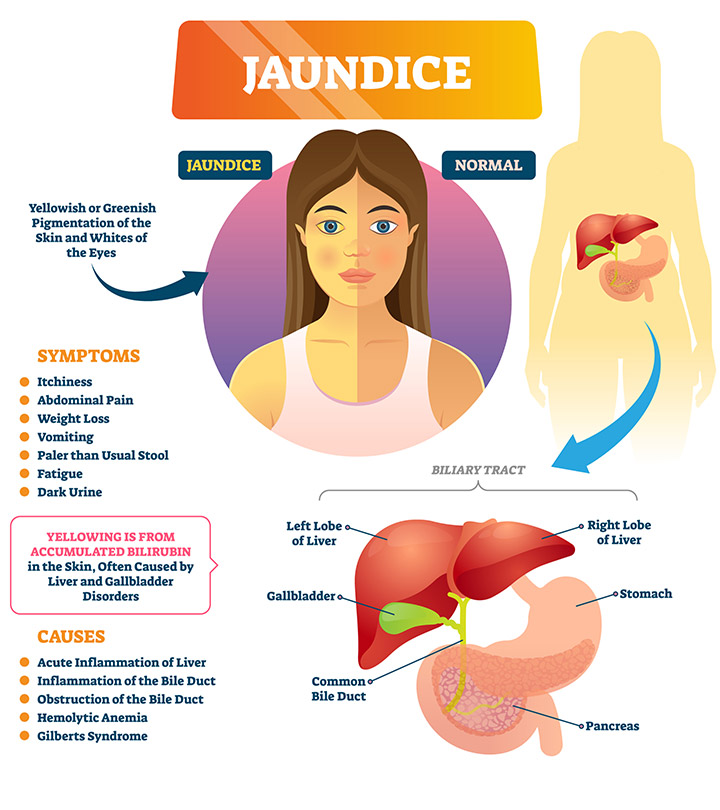
Jaundice in children causes the skin, whites of the eyes (sclerae), and mucous membranes to turn yellow. The yellowish tint usually starts on the face and moves down the body. It is an indication of a condition called hyperbilirubinemia, where a waste product called bilirubin (yellow-orange bile pigment) accumulates in the blood (1) (2).
Jaundice may occur in adults, children, and newborn babies; however, the conditions that cause jaundice in children are different from newborns (3). For example, while jaundice in newborns generally indicates a developing liver, it may indicate a liver disease in older children (1).
Read on about the types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for jaundice in children.
Types Of Jaundice In Children
Jaundice is categorized into three types (4) (5):
- Pre-hepatic jaundice, also called non-obstructive or medical jaundice, is when the bilirubin is produced in excess. It results in the inability of the liver to conjugate and excrete bilirubin into the gut. Pre-hepatic jaundice is commonly caused by hemolytic anemia (for example, sickle cell anemia) that causes accelerated heme breakdown.
- Intra-hepatic jaundice, known as non-obstructive or medical jaundice, happens due to parenchymal liver disease, where the liver loses its ability to conjugate or excrete bilirubin.
- Post-hepatic jaundice also called non-obstructive or medical jaundice, is when the bilirubin is produced in excess. It results in the inability of the liver to conjugate and excrete bilirubin into the gut.
Causes Of Jaundice In Children
Jaundice may develop in children due to the following reasons (1) (6):
- Viral infections, such as hepatitis B and C that cause liver damage
- Liver inflammation caused due to the Epstein Barr virus (7)
- Autoimmune hepatitis, where the body’s immune system attacks the liver cells
- Cirrhosis, is a chronic liver disease where the liver’s healthy tissue is replaced by scar tissue
- Excessive breakdown of red blood cells caused by certain anemia or malaria
- Gallstones (crystals in the gallbladder) obstruct the biliary duct
- A tumor in the bile duct or liver
- Pancreatic cancer and congenital diseases that block biliary ducts
- Wilson disease, where the copper from the food accumulates in the liver
- Adverse effects of medications and toxins in the environment
- Inherited metabolic syndromes, such as Dubin-Johnson, Gilbert’s, and Crigler-Nager syndromes
Symptoms Of Jaundice In Children
The severity of the jaundice symptoms depends on how fast the underlying conditions grow. Apart from the yellowish tinge of the skin, some other common symptoms include (2):
- Flu-like symptoms with fever and chills
- Abdominal pain
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Itchy skin
- Weight loss
- Vomiting (3)
- In the case of Wilson disease, children may display personality changes, disturbed sleep cycle, poor school performance, and inappropriate behavior (3).
Risks Factors Of Jaundice In Children
The factors that increase the risk for jaundice are (3):
- Maternal-infant transmission
- Contaminated blood product transfusion
- Intravenous drug abuse
- High-risk sexual activity
- Travel history
- Infectious contacts in the past
- Misuse of medications, such as acetaminophen
- Family history of jaundice
- Chronic liver disease
Diagnosis Of Jaundice In Children
In most cases, yellow skin and sclerae indicate jaundice in children; however, healthcare providers need detailed information to confirm the condition. Therefore, they start their diagnosis by thoroughly knowing about family and medical history, details of exposure to toxins, recent travels, coexisting symptoms, and duration of jaundice (8).
Further diagnostic tests are also performed, including (2):
- Physical examination to check
- Skin bruises
- Spider angiomas (a lesion with central, red spot and spiderweb-like reddish extensions, indicating liver damage) (9)
- Palmar erythema (a condition that turns palms red)
- Urinalysis or urine testing
- Serum testing to detect complete blood cell count and levels of bilirubin
- Liver function tests
- Ultrasonography or computer tomographic scanning to detect the size and tenderness of the liver
- Liver biopsy in severe jaundice
- Cholangiography (special X-ray procedure to visualize bile ducts) (6)
Treatment For Jaundice In Children
To treat jaundice, the underlying conditions should be treated. The following are the various treatment options depending on the specific cause (6):
- Hemolytic anemia is treated with medications, lifestyle changes, blood transfusion, and bone or marrow transplants (10).
- Infectious diseases are treated with medications.
- Bile obstructions are treated by extracting gallstones, removing tumors, removing gallbladders, and treating pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
- Jaundice, due to Gilbert’s syndrome, is mild and clears out by itself without any treatment (11).
- Pre-hepatic jaundice is treated by infusing immunoglobulins (12).
- Hepatic jaundice is treated with proper nutrition, steroids, and immunosuppressants (12).
- Post-hepatic or obstructive jaundice is treated with surgery (12).
Prevention Of Jaundice In Children
Since jaundice has many causes, it is difficult to prevent jaundice completely. However, some types, such as hepatitis A, could be prevented. Some general tips are (6) (13) (14):
- Keep your children away from industrial chemicals
- Encourage your child not to use any illicit drugs
- Take care not to share needles
- Get your child vaccinated against hepatitis A and B
- Ensure that your child maintains good hygiene and washes their hands regularly, especially before eating or drinking something and after using the toilet
- Encourage your child not to share food and drinks with other people
- Wash utensils, towels, and linens thoroughly
- Drink only bottled water with an unbroken seal during travel
- Avoid eating raw fruits, salads, and undercooked meat during travel
Home Remedies For Jaundice In Children
Children with jaundice also recover faster with some home remedies apart from the prescribed medications. Anecdotal evidence suggests the following remedies for jaundice (15):
- Tomatoes have a carotenoid called lycopene that helps improve liver functioning (16). One glass of tomato juice on an empty stomach in the morning could work. You may add some salt and pepper to it.
- Turmeric assists in treating liver damage due to its yellow pigment called curcumin. (17).
- Sugarcane supports recovery by improving digestion and liver function.
- The juice of raw radish leaves is effective in treating jaundice faster.
- One teaspoon of papaya leaf paste mixed with one teaspoon of honey taken for one to two weeks may treat jaundice.
- Gooseberry effectively treats jaundice because it has high amounts of vitamin C.
- Barley water helps in faster recovery from jaundice.
- The juice of pigeon pea leaves can treat jaundice.
- One cup of beetroot juice, along with some lemon juice, effectively reduces jaundice.
- Drinking fresh carrot juice several times a day helps combat jaundice.
- Taking mashed ripe bananas with honey can help manage jaundice.
- Buttermilk taken with alum and black pepper thrice a day gives good results.
- Bitter gourd and drumsticks are beneficial for children with jaundice.
Diet For Jaundice
Diet plays an important role in helping children recover from jaundice faster. It removes weakness and fatigue and increases energy levels. Some dietary tips include (15) (18):
- Liquid diets are preferable for children during the first four to five days of developing jaundice.
- Provide easily digestible, high carbohydrate food without fats and spices.
- Give frequent small portions of meals.
- Give your children plenty of cooled boiled water. Water helps in removing excess bilirubin from the body.
- Give raw or steamed vegetables and fruits. Avoid giving canned fruit juices.
- When the bilirubin levels decrease, introduce yogurt, porridge, and lean protein such as eggs.
- When the bilirubin levels reach normal, give rice, fish, or lentils. Do not give meat or poultry.
- After taking the advice from the doctor, start adding little oil to the food. However, avoid foods rich in cholesterol and difficult to digest.
- Give your children foods rich in calcium, magnesium, and iron.
Jaundice affects the liver, an important organ of the body. If you see the signs of jaundice in your child, consulting the doctor could only help. Early diagnosis and an effective treatment plan will help prevent complications. Also, ensure your child gets good rest and follows the diet restrictions. Prompt medical support and a good diet are the keys to a faster recovery.
References:
MomJunction’s articles are written after analyzing the research works of expert authors and institutions. Our references consist of resources established by authorities in their respective fields. You can learn more about the authenticity of the information we present in our editorial policy.
The following two tabs change content below.